Control & Basic Operations
Connectivity & network configuration
Raph Rover comes with a built-in router that provides a Wi-Fi access point and can be configured to suit the user's needs. The router supports both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands, allowing for flexible connectivity options. Users can connect their devices to the rover's Wi-Fi network to access the Web User Interface and rover's onboard computer.
To learn how to connect to the Raph Rover's Access Point, follow guide below:
The table below describes rover's network configuration:
| Device | IP Address or hostname | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Router | 10.0.0.1 | The built-in router providing Wi-Fi access point. |
| UPBoard 7000 | 10.0.0.2 or raph.local | The built-in computer running ROS and other software components. Uses mDNS for hostname resolution. |
| RaphCore | raphcore.local | The microcontroller managing low-level hardware functions. Its IP address is not consistent across the rovers but can be accessed via mDNS under the name raphcore.local. |
You can learn how to connect the Raph Rover to an existing Wi-Fi network or configure network settings in the guides below:
Understanding LED panel signals
Raph Rover indicates its current state using LED panels. Understanding these signals can help users diagnose issues and monitor the rover's status.
Normal states
| LED | LED description | State action | State description | Priority |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Green, constant - side panels | Battery state | Indicates current battery level. Can be activated by pressing the POWER button when the charger is disconnected. Each side panel corresponds to a battery on the robot. | 106 | |
| Color corresponding to battery charge, breathing - side panels | Battery charging | Indicates charging and shows current battery charge. When fully charged, the side panel light up green and stops breathing. Charging animation can be disabled by pressing POWER button when charging. | 51 | |
| Color corresponding to battery charge - side panels | Battery connected | Indicates that a battery was connected successfully. | 108 | |
| Red, fading out - side panels | Battery disconnected | Indicates that a battery was disconnected or is fully depleted. | 108 | |
| Blue segment going back and forth - side panels | Micro-ROS connection animation | Indicates that the robot is waiting for Micro-ROS connection. | 60 | |
| White, constant | Rover fully on | Shows that RaphCore is connected to onboard computer. When motors are relaxed a light blue segment will go around the whole LED strip. | 1 | |
| Yellow, constant | Maintenance mode | Indicates that maintenance mode is active. | 90 | |
| Blue, constant | Servo calibration | Indicates that servo calibration is in progress. | 90 |
Fault states
| LED | LED description | State description | Priority |
|---|---|---|---|
| Red, flashing - rear panel | Servo calibration failure | 102 | |
| Red, flashing and fading | Motor communication error | 104 | |
| Red, flashing | Motor fault | 104 |
Fault states also indicate which motor has failed by illuminating the segment of the LED strip that corresponds to the position of the faulty motor, with side panels indicating wheel motors, and rear panel indicating servos.
Controlling the Rover
Raph Rover can be controlled in multiple ways, depending on the needs and preferences. The available control methods are:
- Web User Interface - From the Web UI Raph Rover can be controlled using a gamepad, keyboard or virtual joystick.
- ROS topics - Users can publish commands to the appropriate ROS topics to control the rover's movement programmatically. To see available topics refer to the ROS API documentation.
- Joystick teleoperation - By using the
joy_teleopnode from raph_teleop ROS package, users can control the rover using a gamepad such as an Xbox or PlayStation controller.
Raph Rover supports multiple steering modes:
- Ackermann steering - Suitable for smooth navigation in open areas.
- Turn in place - Ideal for tight spaces and precise maneuvers.
- Ackermann steering
- Turn in place
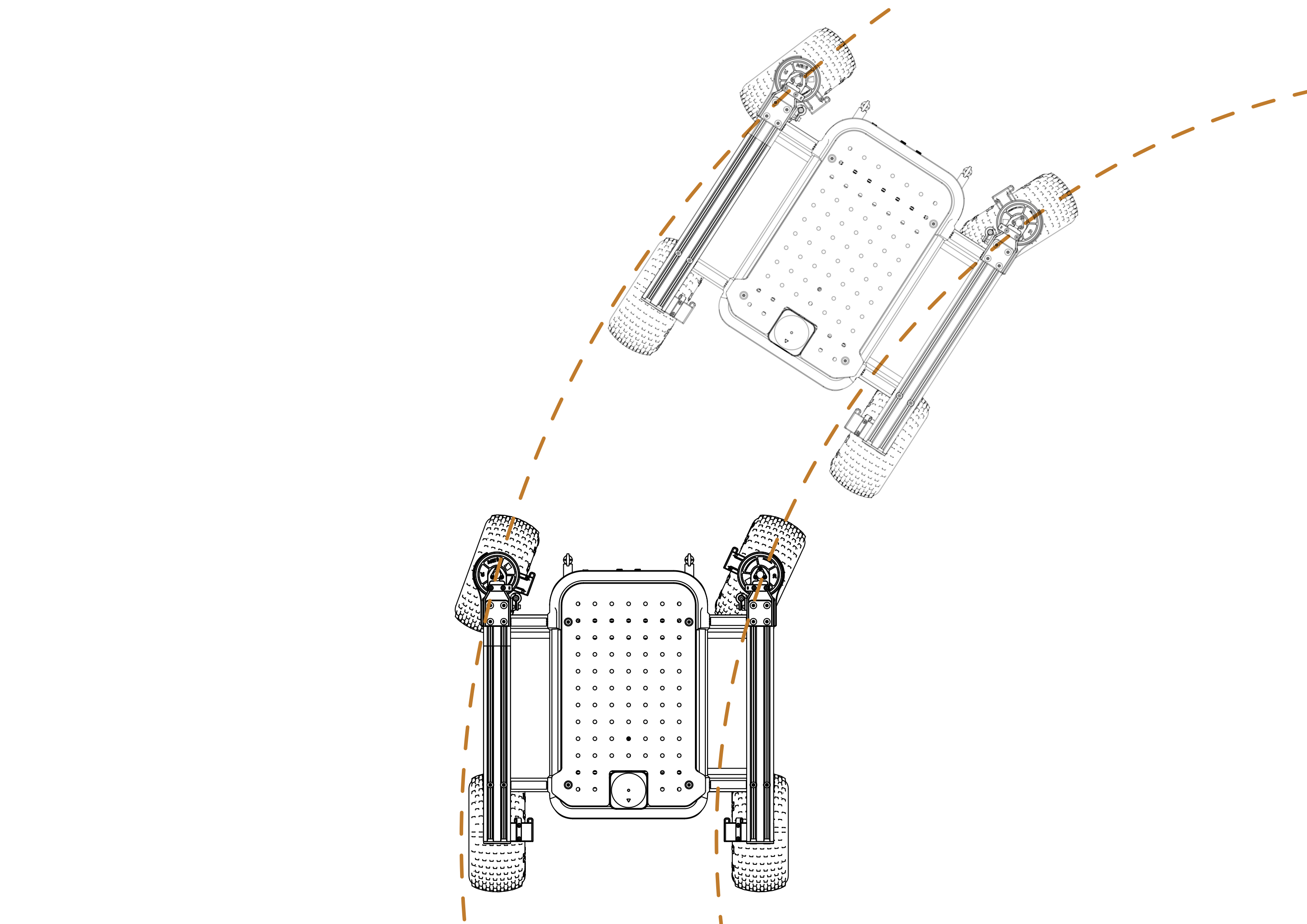

Steering modes can be switched via the Web UI or by calling the
controller/set_steering_mode ROS service.